The Psychological Impact of Auto Accidents: Understanding Trauma and Recovery
Understanding trauma and recovery after auto accidents is vital. It explores PTSD, anxiety, and the importance of therapy, support, and self-care for healing.
Our Network of Attorneys Are Recognized by the Best
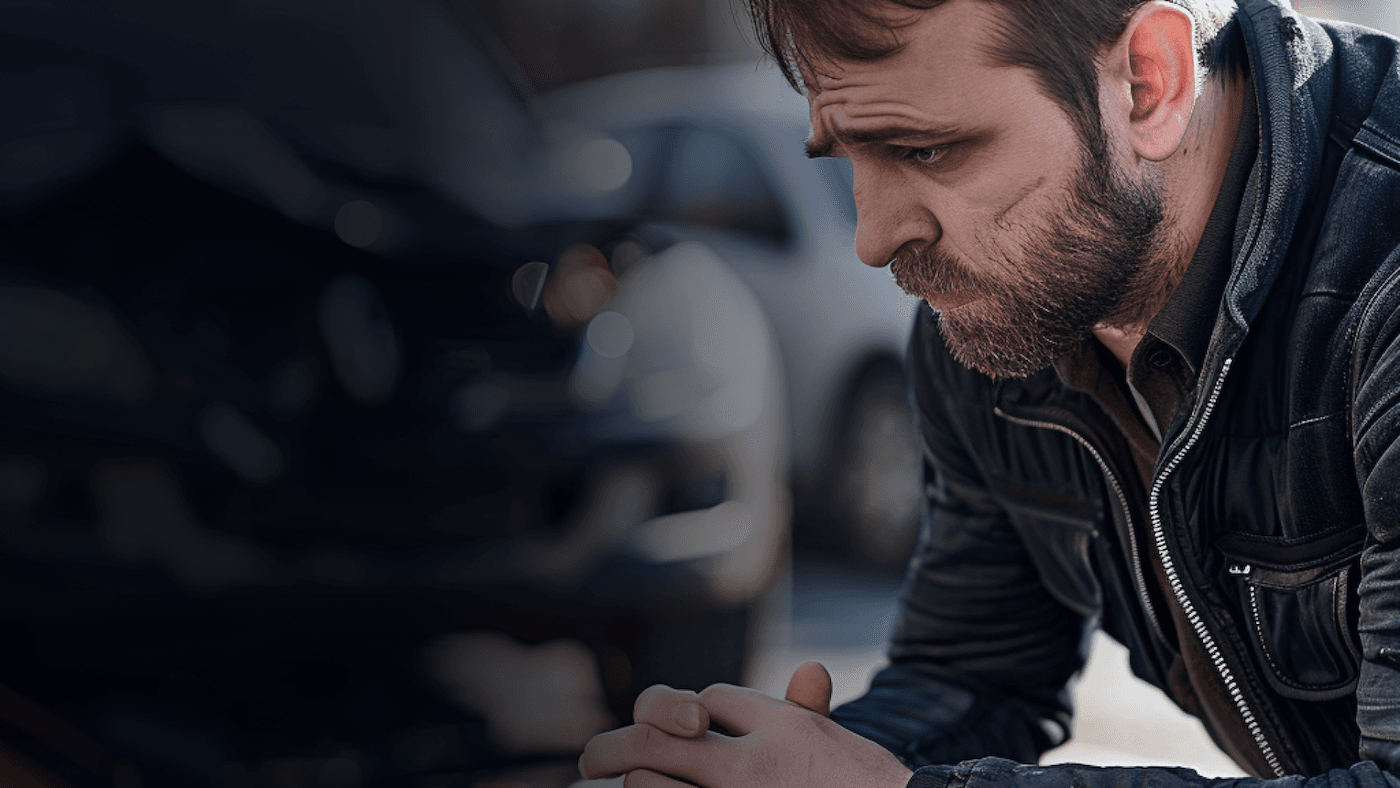
Auto accidents are among the most traumatic events an individual can experience, often leaving lasting psychological effects alongside physical injuries. Understanding these impacts, and the journey towards recovery, is crucial for survivors, their families, and healthcare providers. This article delves into the psychological aftermath of auto accidents, exploring trauma, common mental health conditions that arise, and effective strategies for emotional recovery.
The Immediate Aftermath and Trauma
The immediate aftermath of a car accident is often a period of shock and disbelief. For many, this initial shock eventually gives way to more severe psychological reactions. Trauma can manifest in various ways, ranging from incessant replaying of the event to an overwhelming sense of fear and vulnerability. The most common and distressing emotional condition that can develop is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).
Understanding PTSD
PTSD is characterized by intense, disturbing thoughts and feelings related to the traumatic event that last long after the incident has ended. Individuals may relive the accident through flashbacks or nightmares; they may feel sadness, fear, or anger; and they may feel detached or estranged from other people. PTSD can lead to avoidance behaviors, where the individual steers clear of locations, people, or experiences that remind them of the accident, and can cause hyperarousal – being on constant “high alert.”
Other Common Psychological Responses
Anxiety and Depression
Beyond PTSD, car accident victims might experience a broad range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and phobias, particularly vehophobia, which is the fear of driving. These conditions can emerge even in individuals who have no prior history of mental health issues.
Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)
Similar to PTSD, Acute Stress Disorder involves symptoms like flashbacks, nightmares, and anxiety. However, ASD occurs immediately following the trauma and typically resolves within a month. If symptoms persist, the diagnosis may evolve into PTSD.
The Road to Recovery
Recovery from psychological trauma is a gradual and ongoing process. It often requires a multi-faceted approach that includes therapy, support groups, and sometimes medication.
Seeking Professional Help
Therapy is a cornerstone in treating post-accident psychological effects. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective, helping individuals to process and make sense of their trauma. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is another therapy that has been found to be effective in processing traumatic memories.
The Role of Support Systems
Family, friends, and support groups can provide a network of understanding and compassion that's invaluable for recovery. Sharing experiences with others who have gone through similar trauma can validate a survivor’s feelings and foster a sense of community and understanding.
Self-Care Strategies
Engaging in self-care practices is vital. This includes maintaining a routine, ensuring sufficient rest, engaging in physical activity, eating healthily, and practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques to help manage stress and anxiety.
The psychological impact of auto accidents can be profound and enduring. Recognizing the signs of trauma and seeking timely professional help is crucial for recovery. With the right support and treatment, individuals can rebuild their sense of control and find effective strategies for coping with their memories and fears, embarking on a path toward healing and resilience. The journey might be challenging, but recovery is within reach, leading to a life where the accident is a memory, not a daily reality.